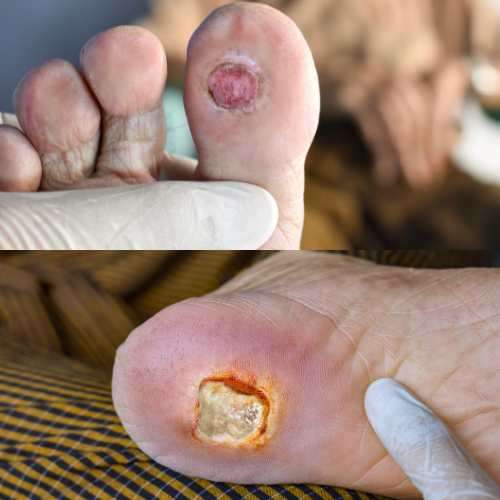
What is Diabetic Foot?
The face, being the most exposed part of the body, plays an important role in determining an individual’s beauty and confidence. Unfortunately, facial injuries resulting from accidents or violence can have devastating effects, not only physically but also emotionally. Soft tissue injuries involving prominent facial features like the nose, lips, and ears, as well as fractures of facial bones such as the jaw and nasal bones, are common occurrences. Dr. Harshvardhan, the best plastic surgeon for facial injuries, specializes in addressing all types of facial injuries with the utmost care and precision, aiming to minimize scarring and restore patients’ confidence Diabetic foot, also known as diabetic foot syndrome, is a common complication of diabetes that can lead to severe health issues if left untreated. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet, making it difficult to feel sensations such as pain, heat, or cold.
Causes and Risk Factors
- High blood sugar levels: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the feet.
- Nerve damage (neuropathy): Damaged nerves can make it difficult to feel sensations in the feet.
- Poor blood circulation: Reduced blood flow to the feet can make it harder for wounds to heal.
- Foot deformities: Conditions like hammertoes, bunions, or Charcot foot can increase the risk of foot ulcers.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the feet.
- Kidney disease: People with kidney disease are more likely to develop diabetic foot.
Symptoms
- Foot ulcers: Open sores on the feet that can be painful or painless.
- Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can occur in the feet.
- Swollen or red feet: Increased blood flow or infection can cause swelling or redness.
- Foul odor: Infected foot ulcers can produce a foul smell.
- Pain or numbness: Pain or numbness in the feet can be a symptom of nerve damage.
Prevention
- Control blood sugar levels: Manage diabetes through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Conduct daily foot exams: Check feet daily for cuts, cracks, or other injuries.
- Wear proper footwear: Wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate support.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep skin hydrated.
- Get regular check-ups: Visit a healthcare provider regularly for foot exams.
Treatment
- Wound care: Clean and dress foot ulcers to promote healing.
- Antibiotics: Treat infections with antibiotics.
- Debridement: Remove dead tissue to promote healing.
- Off-loading: Reduce pressure on the affected area to promote healing.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissues.
Complications
- Amputation: Untreated diabetic foot can lead to amputation.
- Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can spread to other parts of the body.
- Kidney damage: Untreated diabetic foot can lead to kidney damage.
- Heart disease: People with diabetic foot are at increased risk of heart disease.
Conclusion
Diabetic foot is a serious complication of diabetes that requires prompt attention. By controlling blood sugar levels, conducting daily foot exams, and seeking regular medical check-ups, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing diabetic foot. If symptoms occur, seeking medical attention promptly can help prevent serious complications.